transmission system such as telephone lines, copper wires, optical fibres, wireless communication channels, and storage media.
the data can be vary in their presentation..it is either in format of text,voice,still pictures, graphics or even videos.
analogue signal
It is measured in Hertz (Hz).
A signal that is generated by means of a digital modulation method (digital passband transmission), produced by a modem, is in the first case considered as a digital signal, and in the second case as converted to an analog signal.
coMmunication ChanNels
A communications channel is a pathway over which information can be
conveyed. It may be defined by a physical wire that connects
communicating devices, or by a radio, laser, or other radiated energy
source that has no obvious physical presence. Information sent through a
communications channel has a source from which the information
originates, and a destination to which the information is delivered.
Although information originates from a single source, there may be more
than one destination, depending upon how many receive stations are
linked to the channel and how much energy the transmitted signal
possesses.
In a digital communications channel, the information is represented
by individual data bits, which may be encapsulated into multibit message
units. A byte, which consists of eight bits, is an example of a message
unit that may be conveyed through a digital communications channel. A
collection of bytes may itself be grouped into a frame or other
higher-level message unit. Such multiple levels of encapsulation
facilitate the handling of messages in a complex data communications
network.
Any communications channel has a direction associated with it:
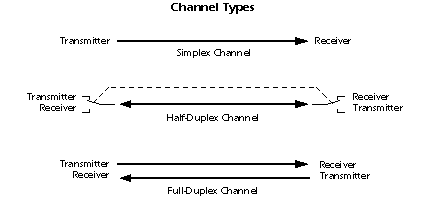
A channel whose direction of transmission is unchanging is referred to as a simplex channel. For example, a radio station is a simplex channel because it always transmits the signal to its listeners and never allows them to transmit back.
A half-duplex channel is a single physical channel in which the direction may be reversed. Messages may flow in two directions, but never at the same time, in a half-duplex system. In a telephone call, one party speaks while the other listens. After a pause, the other party speaks and the first party listens. Speaking simultaneously results in garbled sound that cannot be understood.
A full-duplex channel allows simultaneous message exchange in both directions. It really consists of two simplex channels, a forward channel and a reverse channel, linking the same points. The transmission rate of the reverse channel may be slower if it is used only for flow control of the forward channel.
A multi-plexing channel is the technique that enables more than one device to combine i a time. the network can transfer several different types of data.
-> synchronous & asynchronous systems
In synchronous systems, separate channels are used to transmit data and
timing information. The timing channel transmits clock pulses to the
receiver. Upon receipt of a clock pulse, the receiver reads the data
channel and latches the bit value found on the channel at that moment.
The data channel is not read again until the next clock pulse arrives.
Because the transmitter originates both the data and the timing pulses,
the receiver will read the data channel only when told to do so by the
transmitter (via the clock pulse), and synchronization is guaranteed.
In asynchronous systems, a separate timing channel is not used. The
transmitter and receiver must be preset in advance to an agreed-upon
baud rate. A very accurate local oscillator within the receiver will
then generate an internal clock signal that is equal to the
transmitter's within a fraction of a percent. For the most common serial
protocol, data is sent in small packets of 10 or 11 bits, eight of
which constitute message information. When the channel is idle, the
signal voltage corresponds to a continuous logic '1'. A data packet
always begins with a logic '0' (the start bit) to signal the receiver
that a transmission is starting. The start bit triggers an internal
timer in the receiver that generates the needed clock pulses. Following
the start bit, eight bits of message data are sent bit by bit at the
agreed upon baud rate
wow....so many information..haha
ReplyDelete